ECOO '16 R3 P4 - Cuthbert's Calculator
View as PDFYour friend Cuthbert has a broken calculator. When it was working properly, it had buttons for all decimal digits (
through
), plus three binary operators
, two unary operators
, two memory functions (
store and recall) and a clear button. Binary operators require two operands to produce an answer (e.g. ). Unary operators require only one operand: the
button changes the sign of the number on the screen and displays the result; the
button squares the number on the screen and displays the result. The calculator cannot display more than
digits.
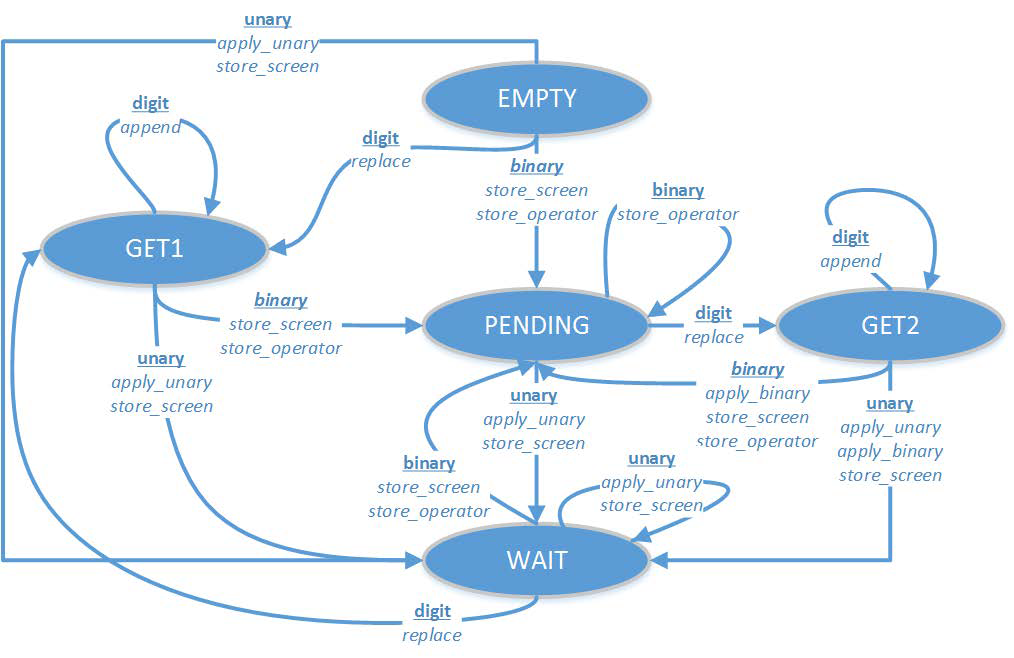
A diagram that describes the basic operation of Cuthbert's calculator is shown below. The calculator starts in the EMPTY state with showing on the screen. When the user presses a key, if it is a digit key, the calculator moves to the
GET1 state. If it's a binary operator , it goes to the
PENDING state. If it's a unary operator it goes into the
WAIT state.
In addition, there are actions the calculator takes on each state transition. For example, if the user presses a unary operator key while the calculator is in the GET2 state, the calculator performs the apply_unary, apply_binary and store_screen operations, in that order, and then moves into the WAIT state. A table that explains these operations is shown below as well.
| OPERATION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
replace |
Replace the contents of the screen with the digit just pressed. |
append |
Add the digit just pressed to the right of the screen. |
store_screen |
Store the contents of the screen in an internal register (X) for later use.
If there is already something in X, it will be replaced. |
store_operator |
Store the operator just pressed in an internal register (OP) for later use.
If there is already something in OP, it will be replaced. |
apply_unary |
Apply the unary operator to the value currently showing on the screen, and update the screen to show the result. |
apply_binary |
Perform the operation in the OP register using the value in the X register
as the left operand and the value currently on the screen as the right operand,
then put the result on the screen. For example, if - and |
The calculator also has two memory buttons MS and MR. The MS button will store the value currently on the screen in the memory register (M). The MR button will copy the value from M to the screen. The MS button does not change the state of the calculator. The MR button moves the calculator to GET1 from EMPTY or WAIT, and to GET2 from PENDING. Otherwise, it also does not change the state.
Finally, there is an AC button which clears the screen to and changes the calculator state to
EMPTY.
Unfortunately, the calculator is broken. Only some of the buttons are working at the moment.
Input Specification
The input contains test cases. Each test case will consist of two lines.
The first line contains the available buttons (some combination of 1234567890+-*ns, where n means negation and s means square). The ac, ms and mr buttons will always be available so they will not be listed.
The second line contains an integer that can be produced on the screen using only the available buttons
.
Output Specification
Your job is to output a sequence of the available keys (in lowercase) such that when all the keys have been pressed in the order you specify, the integer will be shown on the screen.
Special Notes
- Your output needs to go to the file-like object
stdoutand will be scored by an automated judging program. - The solutions shown below are not the only possible solutions.
- The sample input below contains only
cases but the input files will contain
.
Sample Input
012345+-*sn
53
456*-s
78
94s-n
101Sample Output
5 3
5 4 4 - 4 6 6 *
9 - 4 s ms 9 4 - mr -Further Information
Here is a table to help explain the solution to the final sample input above:
| INPUT | STATE | STORED SCREEN | STORED OPERATOR | MEMORY | SCREEN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
EMPTY |
|||||
GET1 |
|||||
PENDING |
- |
||||
GET2 |
- |
||||
WAIT |
- |
||||
WAIT |
- |
||||
GET1 |
- |
||||
GET1 |
- |
||||
PENDING |
- |
||||
GET2 |
- |
||||
PENDING |
- |
Educational Computing Organization of Ontario - statements, test data and other materials can be found at ecoocs.org
Comments