IOI '22 P6 - Thousands Islands
View as PDFThousands Islands is a group of beautiful islands located in the Java Sea.
It consists of
There are
For safety reasons, a canoe needs to be maintained after every time it is sailed, which forbids the same canoe to be sailed two times in a row.
That is, after using some canoe
Bu Dengklek wants to plan a journey through some of the islands. Her journey is valid if and only if the following conditions are satisfied.
- She starts and ends her journey at island
- She visits at least one island other than island
- After the journey ends, each canoe is docked at the same island as it was before the journey.
I.e., canoe
Help Bu Dengklek find any valid journey involving sailing at most
Implementation Details
You should implement the following procedure:
std::variant<bool, std::vector<int>> find_journey(int N, int M, std::vector<int> U, std::vector<int> V)
- This procedure should return either a boolean or an array of integers.
- If no valid journey exists, the procedure should return
false. - If a valid journey exists, you have two options:
- To be awarded the full score, the procedure should return an array of at most
- To be awarded a partial score, the procedure should return
true, an array of more than
- To be awarded the full score, the procedure should return an array of at most
- If no valid journey exists, the procedure should return
- This procedure is called exactly once.
Examples
Example 1
Consider the following call:
find_journey(4, 5, {0, 1, 2, 0, 3}, {1, 2, 3, 3, 1})
The islands and canoes are shown in the picture below.
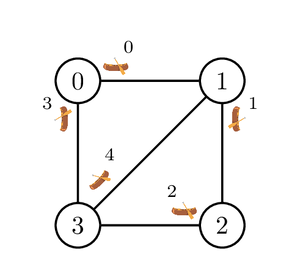
One possible valid journey is as follows.
Bu Dengklek first sails canoes
Therefore, the returned value
Example 2
Consider the following call:
find_journey(2, 3, {0, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 0})
The islands and canoes are shown in the picture below.
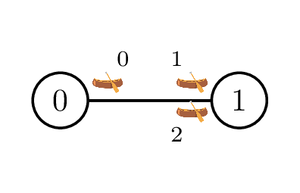
Bu Dengklek can only start by sailing canoe false.
Constraints
Subtasks
- (5 points)
- (5 points)
- (21 points)
- (24 points)
- (45 points) No additional constraints.
For each test case in which a valid journey exists, your solution:
- gets full points if it returns a valid journey,
- gets
true, an array of more than - gets
For each test case in which a valid journey does not exist, your solution:
- gets full points if it returns
false, - gets
Note that the final score for each subtask is the minimum of the points for the test cases in the subtask.
Sample Grader
The sample grader reads the input in the following format:
- line
- line
The sample grader prints your answers in the following format:
- If
find_journeyreturns abool:- line
- line
find_journeyreturnsfalse, or
- line
- If
find_journeyreturns astd::vector<int>, denote the elements of this array by- line
- line
- line
- line
Attachment Package
The sample grader along with sample test cases are available here.
Comments