IOI '24 P5 - Mosaic
View as PDFSalma plans to colour a clay mosaic on a wall.
The mosaic is an
To colour the mosaic, Salma first picks two arrays
Then she repeats the following steps until all tiles are coloured:
- She finds any uncoloured tile
- Then, she colours tile
It can be shown that the final colours of the tiles do not depend on the order in which Salma is colouring them.
Yasmin is very curious about the colours of the tiles in the mosaic.
She asks Salma
- Topmost row
- Leftmost column
The answer to the question is the number of black tiles in this subrectangle.
Specifically, Salma should find how many tiles
Write a program that answers Yasmin's questions.
Implementation Details
You should implement the following procedure.
std::vector<long long> mosaic(
std::vector<int> X, std::vector<int> Y,
std::vector<int> T, std::vector<int> B,
std::vector<int> L, std::vector<int> R)
- The procedure should return an array
- This procedure is called exactly once for each test case.
Constraints
Subtasks
| Subtask | Score | Additional Constraints |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | No additional constraints. |
Example
Consider the following call.
mosaic([1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0, 1], [0, 2], [3, 3], [0, 0], [3, 2])
This example is illustrated in the pictures below. The left picture shows the colours of the tiles in the mosaic. The middle and right pictures show the subrectangles Yasmin asked about in the first and second question, respectively.
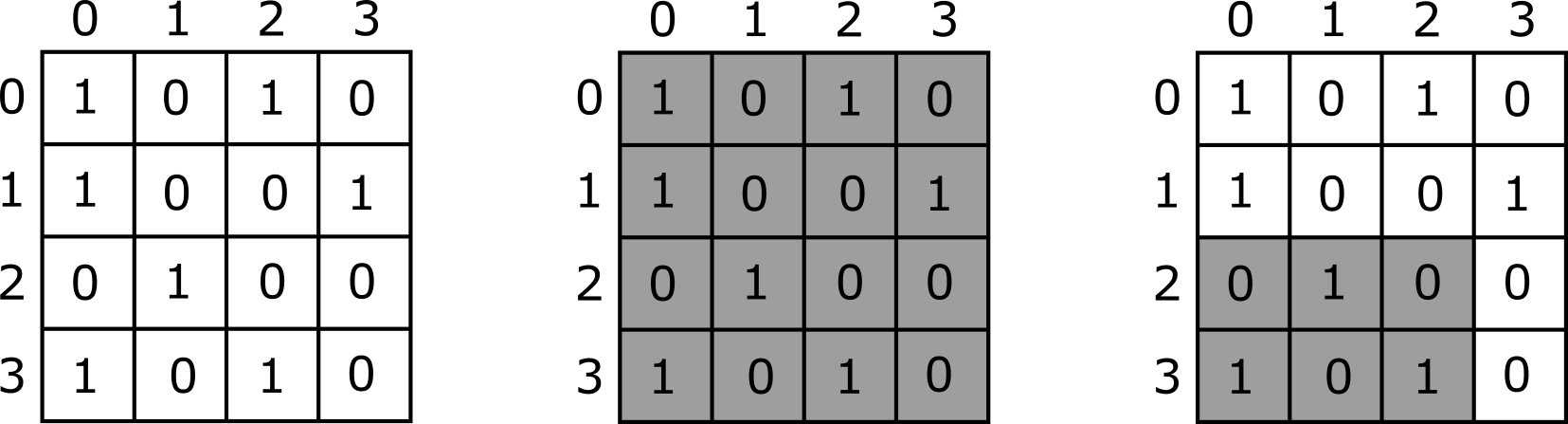
The answers to the questions
(that is, the numbers of ones in the shaded rectangles)
are 7 and 3, respectively.
Hence, the procedure should return
Sample Grader
Input format:
N
X[0] X[1] ... X[N-1]
Y[0] Y[1] ... Y[N-1]
Q
T[0] B[0] L[0] R[0]
T[1] B[1] L[1] R[1]
...
T[Q-1] B[Q-1] L[Q-1] R[Q-1]Output format:
C[0]
C[1]
...
C[S-1]Here, mosaic.
Attachment Package
The sample grader along with sample test cases are available here.
Comments